PM Modi Launches ₹1 Lakh Crore Rozgar Yojana to Boost Youth Employment
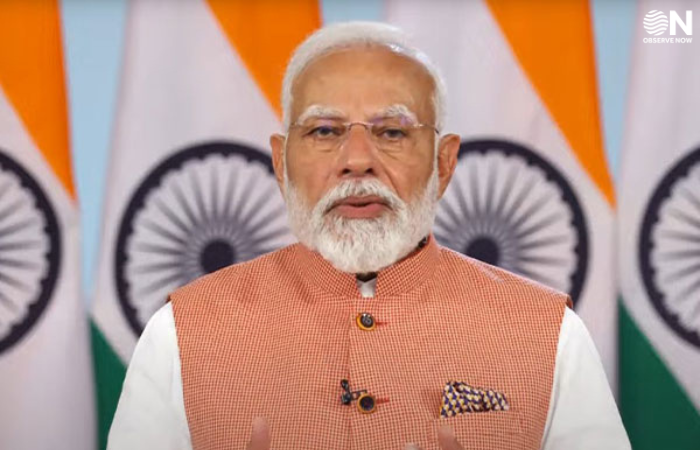
On August 15, 2025, Prime Minister Narendra Modi unveiled the Pradhan Mantri Viksit Bharat Rozgar Yojana (PMVBRY), a flagship employment scheme aimed at creating millions of job opportunities for the country’s youth. Announced on India’s 79th Independence Day, the ₹1 lakh crore initiative is designed to generate 3.5 crore new jobs by July 2027, marking a significant step in addressing the challenges of youth unemployment in India. The program is structured to support both first-time job seekers and private sector employers, with targeted financial incentives encouraging broader participation in the workforce.
The scheme provides a ₹15,000 financial incentive for individuals securing their first private sector job. By directly supporting newcomers to the workforce, the government intends to ease the transition from education or vocational training to gainful employment. This approach not only benefits the youth but also strengthens the talent pipeline for businesses looking to hire motivated and skilled employees. The initiative reflects a long-term strategy to reduce unemployment while simultaneously fostering economic growth across multiple sectors.
Employers in the private sector are also set to benefit under PMVBRY. Companies that create new positions for first-time employees will receive monetary support, up to ₹3,000 per employee per month, for a period of at least six months. This dual-incentive model aims to stimulate job creation, encouraging businesses to expand their workforce while ensuring that young professionals gain essential work experience. By aligning the interests of both job seekers and employers, the government seeks to create a sustainable ecosystem for employment generation.
The Rozgar Yojana covers jobs created between August 2025 and July 2027, with a particular focus on first-time job entrants. The program is expected to generate employment across various industries, including manufacturing, services, and technology. By linking financial support to actual job creation, the scheme ensures accountability and tangible impact, helping the nation meet its ambitious employment targets.
Beyond immediate job creation, the initiative is seen as a step toward long-term economic empowerment. By incentivizing both employment and skill development, PMVBRY encourages a culture of formal work and professional growth. Young workers entering the formal economy will gain access to social security benefits, structured career paths, and a more predictable income, all of which contribute to economic stability and societal progress.
The launch of the PMVBRY represents a broader vision of a developed and self-reliant India, where youth have the tools, opportunities, and support to thrive. By combining government backing with private sector participation, the scheme aims to address unemployment challenges while preparing the workforce for future economic demands. It underscores the government’s commitment to youth development, skill enhancement, and job creation as key drivers of national growth.
With this ambitious initiative, India takes a major stride toward equipping its young population with meaningful employment opportunities, creating a foundation for sustained economic growth, and realizing the aspirations of millions of its citizens.